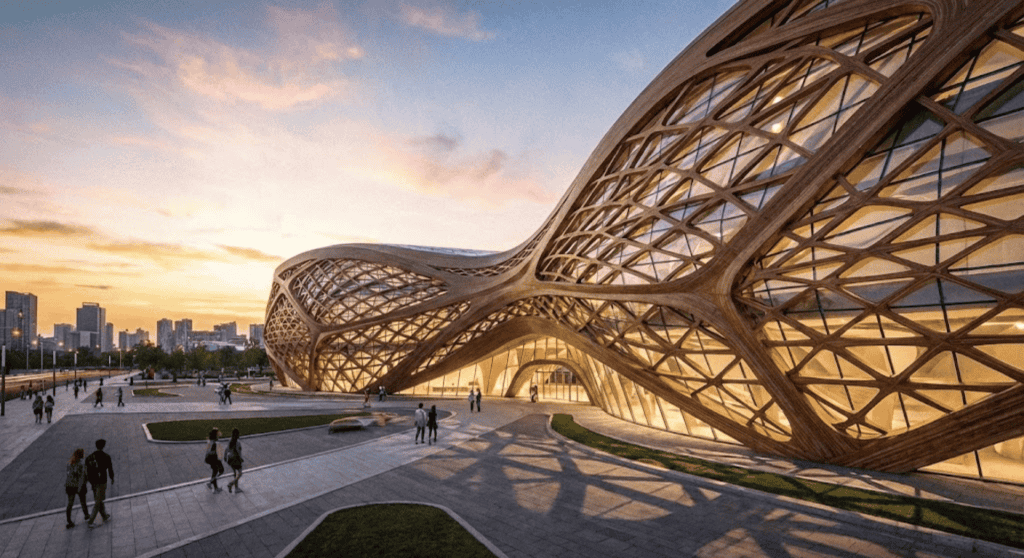
Mass timber construction represents a revolutionary shift in sustainable building practices, enabling wooden structures to reach heights previously reserved for steel and concrete. Engineered wood products like cross-laminated timber (CLT) and glulam combine renewable materials with advanced manufacturing to deliver strong, lightweight, carbon-sequestering building systems for tall structures.
Key Insights on Mass Timber Construction:
- Carbon Storage: Trees absorb CO2 during growth, and mass timber buildings lock this carbon for decades, creating carbon-negative structures when sourced from sustainably managed forests.
- Structural Performance: Engineered timber products achieve strength-to-weight ratios comparable to steel while offering excellent seismic resistance through controlled flexural behavior.
- Construction Speed: Prefabricated timber panels enable rapid assembly with minimal wet trades, reducing construction timelines by 25-30% compared to conventional methods.
- Fire Safety: Contrary to intuition, mass timber exhibits predictable charring behavior that maintains structural integrity during fires, meeting stringent building code requirements.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Exposed timber interiors create warm, biophilic environments that improve occupant well-being and provide distinctive architectural character.
- Design Limitations: Current building codes in many regions restrict timber building heights, though regulations are evolving as research demonstrates safety and performance capabilities.
India Context Example:
While India’s mass timber sector is emerging, the IIT Roorkee has established a Centre of Excellence in Mass Timber Construction to develop standards and promote engineered wood technology suited to Indian conditions, including bamboo-based mass timber products that leverage local resources.
Practical Conclusion:
Mass timber offers architects a sustainable alternative for mid-to-high-rise construction, particularly suitable for regions with sustainable forestry practices. Early engagement with structural engineers, fire safety consultants, and regulatory authorities is essential to navigate evolving codes and realize timber’s full potential as a low-carbon building solution.
Reference: Forest Products Laboratory, USDA